CFDs are complex instruments and come with a high risk of losing money rapidly due to leverage. 77% of retail investor accounts lose money when trading CFDs with this provider. You should consider whether you understand how CFDs work and whether you can afford to take the high risk of losing your money.
Commodity Trading: A Beginner’s Guide
Open Account Open Demo AccountTrading is risky. Your Capital is at risk.
Want to trade commodities? The truth is commodity trading is profitable. Crude oil, natural gas, and spot metals are available as CFDs. In this article, learn about commodities, markets, and how to trade like an expert.
What Are Commodities?
A commodity is a real asset available in measurable physical quantities. Popular examples include primary agricultural products, such as corn, soybeans, or dairy products. Trading takes place on international commodity market exchanges, like the New York Mercantile Exchange (NYME).
What is commodity trading?
It describes the purchasing or selling of commodities. Transactions fall into two categories:
Physical Commodity Trading
During the trading, buyers exchange physical commodities with sellers. Trading is based on spot prices. For example, an investor may visit a precious metal website such as JM Bullion. After buying gold bars, delivery takes place. Oil companies may also buy and store oil barrels to sell later.
Derivatives Commodity Trading
Traders may buy and sell swaps, futures, forwards, and options. They are derivative financial instruments based on underlying assets.
What Are the Different Categories of the Commodity Market?
In reality, the commodity market is not one marketplace. Rather, it’s various regulated futures exchanges. What happens in the exchange? Hedgers (commodity companies, retailers, or manufacturers) buy future(s?) contracts created by the exchange. Their aim is to offset the risk associated with price changes. Speculators and traders look to buy and sell high.
In the past, most trading took place on the trading floor. Electronic trading now dominates. Examples of London commodity markets include the London Commodity Exchange (LCE) and London Metal Exchange (LME). The most traded commodities, in order of popularity, include West Texas Intermediate (WTI) crude oil, coffee, natural gas, gold, Brent Oil, silver, sugar, corn, wheat, and cotton.
Commodities with the highest trading activity are the best commodities to trade as CFDs. They are highly volatile with high price swings. Various commodity markets include:
Commodity Futures
Futures are legally-binding contracts created and helped by a regulated exchange. What's agreed? One party agrees to buy a predefined quantity of commodities. Delivery takes place at a future date, several weeks, months, or years later. Future prices are set during the price discovery process of quoting and bidding. The contract also specifies the quantities and delivery location.
One party assumes the risk of price changes. For instance, an oil speculator may enter a futures contract to buy 5,000 barrels of oil at $20 a barrel. In the coming months, oil prices per barrel may fall to $15. The buyers still need to pay $20 on delivery. When they sell oil, they make a loss. If prices rose to $25, they would turn (make?) a profit.
Commodity Forwards, Swaps, and Options
They are future contracts but with different contract specifications. Forwards, for instance, allow participants to customize quantities and delivery dates. Options on futures contracts mean that the parties only have a right, not an obligation, to follow through with the contract terms. Swaps facilitate the change of cash flows based on the value of the underlying assets.
Exchange-traded Funds & Mutual Funds
Commodity ETFs are a basket of commodities. Traders may buy and sell ETFs like shares on a stock exchange. The ETF fund may own the physical commodity or its future contracts. Investors share ownership of the fund. An example includes the SPDR Gold Shares ETF designed to track the prices of gold.
Trading Commodities with FXTM
Trading futures or buying ETFs come with a higher barrier of entry. Consider, for instance, that the standard contract size for WTI crude oil futures is 1,000 barrels.
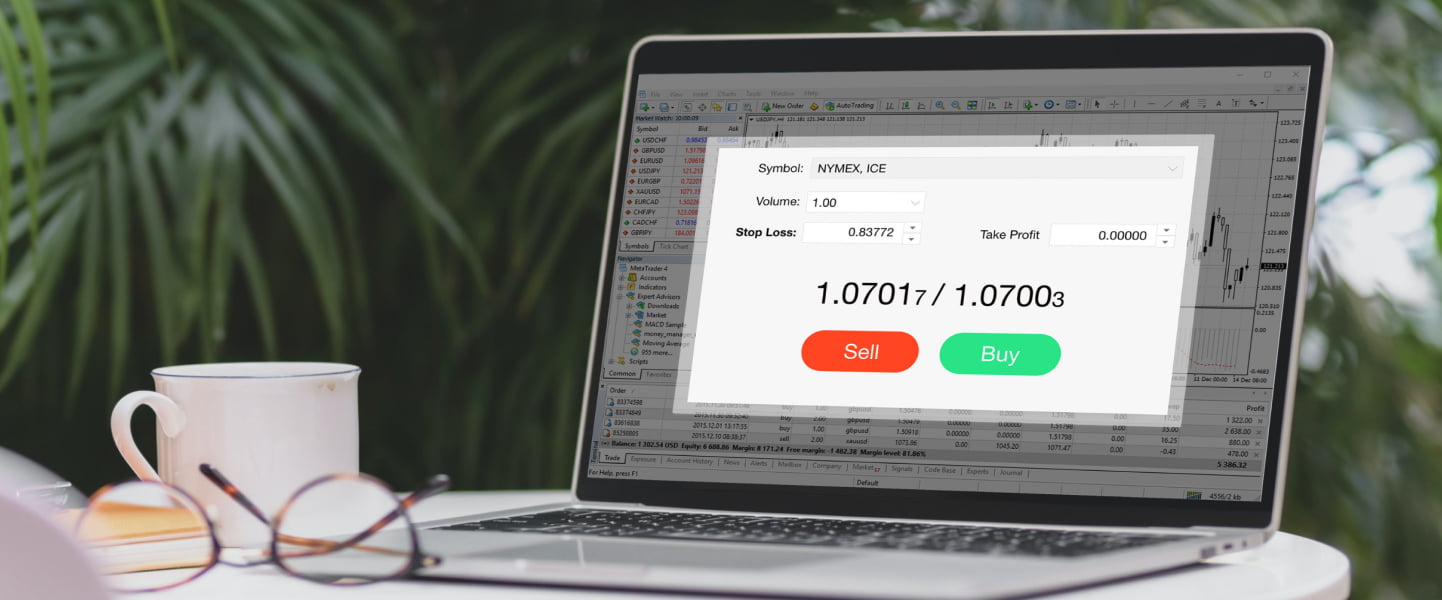
FXTM gives traders a faster way to make money with commodities. Traders just need to trade (the?) CFDs commodities index. Like Forex trading, they speculate if commodity prices will rise or fall. There is nothing to own. Getting started doesn't require membership to a regulated exchange or fund sponsor.
It’s the current price of a given asset in a particular marketplace. The difference is the futures price. So, why trade commodities at FXTM?
- Leverage: Traders may open larger positions using the multiplication effect of leverage. For US natural gas, the leverage is up to 1:19 or 1:52 with US crude oil.
- To diversify your portfolio.
- Access to popular commodity markets and commodities index.
- Low margin requirements.
- Competitive spreads ranging from 4 to 11 pips.
Agricultural Commodities
The agricultural commodities market is one of the most heavily traded. But trading oil takes first spot. Most of the trades take place around futures, options, and commodity indexes. Major categories include:
- Grains & oilseeds: Products include corn, wheat, barley, oats, Black Sea corn, soybean, and rough rice.
- Dairy: They are daily and milk products, including cash-settled cheese options, Class III milk options, non-fat dry milk options, and Class IV milk options.
- Fertilizer: There's a thriving international global fertilizer business. The most-traded products include futures and cleared swaps, for instance*, Urea (Granular) futures and UAN FOB NOLA Swaps.
- Lumbers and softs: Lumbers refer to softwood from coniferous trees. Softs are coffee, sugar, and cocoa futures.
Metal Commodities
Traders may buy and store gold bars or coins. Metal trading involves buying and selling futures and options. Indirect investments may entail buying and holding ETFs or joining mutual funds. A commodity ETF is also a stock market commodity, bought and sold like shares.
Metal commodity categories include:
- Precious metals: The COMEX exchange is the leading marketplace for trading precious metal futures. They include gold, platinum, silver, and palladium. Precious metals are ideal for portfolio diversification or hedging against inflation. When the dollar is falling due to inflation, the price of gold increases due to demand.
- Base metals: They are nonferrous (without any iron). Popular trading products include Copper Futures and Aluminium Futures.
- Ferrous metals: The ferrous metals market ranks second after the global energy industry. Prominent products include steel and iron ore futures and options.
Livestock Commodities
Livestock commodity exchange entails trading futures based on the value of the underlying farm animals. Most trading revolves around cattle and pigs on markets such as Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME).
The most traded futures commodities contracts on the CME exchange include:
- Live cattle options - Cattle ready for slaughter and more than 1,050 pounds in weight.
- Lean hog options - Hogs at about 250 pounds in weight and ideal for slaughter.
- Feeder cattle options - Weaned calves not more than 800 pounds.
- Pork Cutout options - Pork carcass cutouts, e.g., loins, ribs, or ham.
Energy Commodities
Energy commodities present favorable opportunities for speculators and hedgers. Crude oil prices, for instance*, tend to be highly volatile. Changing demand, the health of the economy, pipeline changes, and political events all affect the price of crude oil
Also, long-term events influence global energy trends. For instance*, the rising US oil production, increased Asian demand, population increases, and growth of developing economies.
Examples of energy commodities include crude oil, gasoline, heating oil, natural gas, ethanol, and uranium (for nuclear energy). You may trade energy CFD commodities on popular markets that include:
- Brent Crude Oil: The oil comes from North Sea oil fields off the coast of Europe. Denoted as sweet and light, it produces diesel and gasoline. Its futures are traded on the Intercontinental Exchange (ICE). Brent oil acts as the leading indicator of global oil prices.
- WTI Crude Oil: West Texas Intermediary (WTI) is the second most traded crude oil. About 1.2 million WTI futures exchange direct on the NYMEX exchange, provided by the CME group.
- Natural gas: Henry Hub Natural Gas (NG) Futures are traded on the NYMEX exchange. NG futures rank third as the most traded physical commodity futures by volume.
Undated Commodities Vs. Commodity Futures
Commodity contracts specify the terms of delivery. For instance*, in commodity futures trading, contracts have a set delivery date in the future. Upon the expiry date the contract simply no longer holds or exists. When a futures contract expires, you can’t trade it anymore. For instance*, if you have a futures contract and it expires, the supplier is obligated to deliver the commodities.
In the case of oil, the trader may receive a delivery notice, informing of the collection point of barrels of oil. Most futures contracts are closed or sold before the expiry date. Traders mostly sell off the futures to realize a profit or roll over the contract.
Undated commodities are contracts without expiry dates. They can’t expire because they don’t involve direct ownership of real assets, for instance, trading commodity CFDs. Some companies that participate in commodity futures markets may see the contract through the expiry date if they want to take ownership of the underlying assets, for instance*, manufacturers or wholesalers.
How Can I Improve My Commodity Trading Results?
Improve your commodity trading results by implementing these tips:
Get Educated
Looking for the best commodity finance education? We have several recommendations. First, try the CME Group education courses. They are behind the largest commodities futures markets.
Go to their main website, and from the menu, choose the "Education" tab. Besides courses and lessons, they have training simulators and various challenges. You can also follow different markets and obtain detailed explanations of global commodities.
Ice Markets is a reliable source of information on the global oil market. Catch their monthly oil reports and learn about the global oil benchmarks. They also publish informative articles and podcasts about the oil industry.
Investopedia gives detailed explanations of various terms and topics. Closer to home, ForexTime also publishes webinars and expert insights.
Analyze the Commodity Market
For success in world commodity trading, build up your market analysis skills. First, take advantage of fundamental analysis. It may involve monitoring and gauging the impact of economic news releases. Traders use an economic calendar for this purpose. Watch the economic health of a country, key oil producers, and geopolitics. Read market reports from trading exchanges, including ICE or CME.
For instance, meetings and announcements by OPEC have an immediate effect on oil prices. Why? Members of the trade organization collectively account for 40% of the world’s oil supply.
Develop your fundamental analysis skills, too. Analyzing charts to spot price patterns or trends provides short-term trading signals. You can learn more about:
- Momentum indicators
- Moving averages
- Scholastic indicators
- Relative strength indicators
- Bollinger bands
- Moving average convergence divergence (MACD).
Manage Your Risk
Speculating on price movements involves risking your capital. Using leverage also multiplies your risk. For proper risk management, when you trade commodities:
- Set up stop-loss orders: The S/L restricts your losses to an amount you're comfortable losing on a trade.
- Trailing stops: The trailing stop is essentially a moving stop-loss order that trails or follows the price movement. Rather than specifying a specific limit price, you place the trailing stop several points from the current price.
- Risk vs reward ratio: It's the amount you stand to gain for each unit of currency invested. For instance, a ratio of 1:2 signifies that you might gain $2 for risking $1, or 10 pips for risking 5 pips. An ideal ratio is 1:3.
Diversify Your Portfolio with Commodities
If you're currently trading forex pairs, should you add commodities to your portfolio? What advantages does this commodity trading strategy bring?
Trading commodities with currency pairs may reveal a correlation in the prices. It's widely known, for instance*, that the price of oil is inversely correlated to the US dollar. An increase in oil prices up to 10% may lead to a depreciation of the US dollar. A weakening US dollar may cause an increase in oil prices.
Certain currencies around the world are chosen as "commodity currencies." Fluctuating commodity prices and export values influence price movements of the currencies.
Retail traders looking to sell or buy commodities as CFDs will also appreciate that commodities are more volatile than currency pairs and stocks. They can greatly profit by making correct price predictions.
Choosing a Broker
Use these rules to find the best commodities broker:
Rule 1: Are They Reliable and Trusted?
Many online commodity brokers allow traders access to commodities markets via CFD trading. But make sure that they have the right regulatory compliance. Check their safeguards that guarantee the safety of your funds
Rule 2: Availability of ECN and Standard Accounts
Brokers may be dealing or non-dealing brokers/ECN brokers. A non-dealing broker doesn't take opposing positions against you. In some sense, it eliminates competition. ECN accounts are also the most favorable if you're using Expert Advisors/Trading robots.
Rule 3: Favorable Brokerage Fees
Make sure that you're paying a fair market rate. For ECN broker accounts, traders pay spreads and commission. For standard accounts, you only pay for spreads.
Rule 4: Availability of Commodity Trading Instruments
Choose a broker that provides access to the key commodities, including natural gas and crude oil.
Rule 5: Education, Expert Advice, and Trading Tools
The right trader should provide additional resources and value. Check out if they publish educational videos, articles, webinars, or market analysis.
FAQ
Learn more about commodity trading with these quick questions and answers. For more/extra help, you can always contact us.
What is a Commodity?
The term commodity is used to describe raw materials, extracted minerals, or agricultural outputs. They are bought and sold on the spot market or act as the basis of other derivatives markets such as the futures market.
What do Commodity Traders Do?
Commodity traders may directly invest in commodities, such as buying physical gold bars or trading futures contracts. They can also speculate on the price movements of commodities through CFD trading.
What are the Margin Rates on Commodities?
The margin refers to the amount of money that should be in your trading account balance to open positions on various commodities. Margin rates differ from broker to broker. ForexTime offers a leverage of up to 1:200 on spot metals with a floating margin of up to 0.5%.
How to Become a Commodity Trader?
Commodity traders may join commodity exchanges to take part in trading futures, swaps, or options. Or, you may become a commodity trader by signing up to a broker that offers CFD trading.
What is the Most Profitable Commodity?
The most profitable commodities are characterized by high liquidity and volatility. So, the best commodities to invest in or trade include natural gas, crude oil, and spot metals.
Which Trading is Best: Equity or Commodity?
Suitability is dependent on the goals of the trader. Equity investing is more long-term, as traders may hold stocks or ETFs for several years. Purchasing futures is also considered a short-term trading strategy. Similarly, trading commodity CFDs is more short term and devoid of various expenses & stick requirements.
How Can FXTM Help?
FXTM can help you start commodity trading with ease. You don't need to go through a commodities exchange. There is no need to buy commodities index through ETFs or invest large sums by joining mutual funds.
Traders benefit through fast execution on all transactions. This minimizes the chances of slippage. By partnering with various liquidity providers, we also guarantee customers the best bid and ask prices.
New traders are free to use automated expert advisors. We also provide the industry-leading trading platforms, MetaTrader 4 and 5. By using leverage, you may open large trades even with a modest account balance. You also get the best support and access to educational materials.
Starting is quick and easy. Just sign up and start trading for free with a demo account on FXTM!